How to Find Router IP Address with Command Prompt. Click the Windows search bar, and type Command Prompt in the search box. Then press Enter. You can also double click on the Command Prompt app that appears in the search results. Type ipconfig in the command line and press Enter. You will see your. An IP (Internet Protocol) address is a number assigned to a piece of hardware on a network, such as your router, computer, or mobile device. Your cell phone has a unique phone number assigned to it so you can use it to make and receive calls. If you can find out the IPv4 or IPv6 address of an Internet user, you can get an idea what part of the country or world they're in by using our IP Lookup tool. What to do: Enter the IP address you're curious about in the box below, then click 'Get IP Details.'
- How To Check Modem Speed
- How To Check Modem Ip Address Ip
- Find My Router Ip Address Windows 10
- How To Check Modem Ip Address 192 168
One type of popular and well established modems are Motorola Surfboard (Arris) Modems. These modems have been a popular choice for both cable providers and users who purchase their own. Accessing your modem can give you a good indication of possible issues arising from inadequate signal strength or too much noise on the line that will affect the connection.
By accessing the screen pages inside your modem you should be able to gain some information on your Internet connection. Two important pages are the Status page and the Signal page, both showing a snapshot of information about your current Internet provider's Internet signal strength and potential possible issues that could affect your connection and ultimately your VoIP service.
Steps to access your Arris Surfboard Modem and check signal levels to troubleshoot your connection.
- Start by accessing your Arris surfboard cable modem by opening your web browser and using the IP address of 192.168.100.1 (This address is also used for older Surfboards.). Once open it should show you The default page the Status page. The most important information on this page is The Cable Modem Status which should show Operational. If a Failed appears above this information and the modem does not show Operational then the modem has failed to sync with the Cable Provider and is not connected. An Operational modem can also be determined by looking at the modem indicator lights with the Online light being solid.
- The next page to get useful information and probably the most important one is the Signal page which will show certain power levels which can give an indication of a problem.
Information when troubleshooting cable modem signal levels.
Poor signal levels result in- Signal levels that are not in the acceptable parameters listed above can cause loss of connection, slow speeds and connection issues, including failure of one of the steps needed for registration with the provider, packet loss or the need for packet retransmission.
Premise hardware- On premise hardware including splitters, bad connectors, and poor quality cabling will effect cable signal levels and can cause problems. The cable modem should be a direct line from the first splitter using the leg with the least dB loss. This will allow the best level of signal from the cable box at the premise to reach the modem.
Signal level variation- Checking the modem's signal levels is a snapshot of those levels at that time. Weather and the change of temperatures affects cable hardware which can reflect in variations of the levels at the modem. It is recommended that for best performance some headroom is included in a modem's levels of approximately 3dB. Additionally, when checking the modem and finding variations that occur in a short period of time, where the signal level readings are varying sporadically is a cause for concern and may point to an issue that needs to be corrected.
Services Best SolutionsHow to Locate IP, Gateway, Subnet and DNS Information
An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a unique number that can identify each host (computers, routers, switches, etc.) on a network. When a host sends information to the IP address of a second receiving host it includes IP of origination, IP of destination and other information. Knowing the IP address of key network components such as routers, firewalls and servers, can be useful when troubleshooting network problems. Use of utilities like Ping or Trace Route can help isolate problem areas.
A knowledge of relevant network topology and settings including DNS, gateway and subnet mask can also be useful when exploring network issues.

Domain Name Service (DNS) numbers are IP addresses that a workstation or server uses to refer to specific servers that resolve domain names to IP addresses.
A gateway IP refers to a device on a network which sends local network traffic to other networks.
The subnet mask number helps to define the relationship between the host (computers, routers, switches, etc.) and the rest of the network.
System Requirements
IP addresses are a part of the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) suite of protocols and will be present on every system that is connected to the Internet. The IP protocol is installed by default on most operating systems.
Windows 95/98
Select Start >Programs >DOS Prompt
In the resulting command line window, type winipcfg.
A new window will open up displaying IP network information for that host.
In the first selection box, click on the down arrow and select the proper network interface. There will be a network connection listed for a dial-up, and one listed for each network card installed in the computer.
Click on the More Info button to see additional IP information.
To view additional DNS information click on the box next to the first DNS number marked '...'.
- Start by accessing your Arris surfboard cable modem by opening your web browser and using the IP address of 192.168.100.1 (This address is also used for older Surfboards.). Once open it should show you The default page the Status page. The most important information on this page is The Cable Modem Status which should show Operational. If a Failed appears above this information and the modem does not show Operational then the modem has failed to sync with the Cable Provider and is not connected. An Operational modem can also be determined by looking at the modem indicator lights with the Online light being solid.
- The next page to get useful information and probably the most important one is the Signal page which will show certain power levels which can give an indication of a problem.
Information when troubleshooting cable modem signal levels.
Poor signal levels result in- Signal levels that are not in the acceptable parameters listed above can cause loss of connection, slow speeds and connection issues, including failure of one of the steps needed for registration with the provider, packet loss or the need for packet retransmission.
Premise hardware- On premise hardware including splitters, bad connectors, and poor quality cabling will effect cable signal levels and can cause problems. The cable modem should be a direct line from the first splitter using the leg with the least dB loss. This will allow the best level of signal from the cable box at the premise to reach the modem.
Signal level variation- Checking the modem's signal levels is a snapshot of those levels at that time. Weather and the change of temperatures affects cable hardware which can reflect in variations of the levels at the modem. It is recommended that for best performance some headroom is included in a modem's levels of approximately 3dB. Additionally, when checking the modem and finding variations that occur in a short period of time, where the signal level readings are varying sporadically is a cause for concern and may point to an issue that needs to be corrected.
Services Best SolutionsHow to Locate IP, Gateway, Subnet and DNS Information
An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a unique number that can identify each host (computers, routers, switches, etc.) on a network. When a host sends information to the IP address of a second receiving host it includes IP of origination, IP of destination and other information. Knowing the IP address of key network components such as routers, firewalls and servers, can be useful when troubleshooting network problems. Use of utilities like Ping or Trace Route can help isolate problem areas.
A knowledge of relevant network topology and settings including DNS, gateway and subnet mask can also be useful when exploring network issues.
Domain Name Service (DNS) numbers are IP addresses that a workstation or server uses to refer to specific servers that resolve domain names to IP addresses.
A gateway IP refers to a device on a network which sends local network traffic to other networks.
The subnet mask number helps to define the relationship between the host (computers, routers, switches, etc.) and the rest of the network.
System Requirements
IP addresses are a part of the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) suite of protocols and will be present on every system that is connected to the Internet. The IP protocol is installed by default on most operating systems.
Windows 95/98
Select Start >Programs >DOS Prompt
In the resulting command line window, type winipcfg.
A new window will open up displaying IP network information for that host.
In the first selection box, click on the down arrow and select the proper network interface. There will be a network connection listed for a dial-up, and one listed for each network card installed in the computer.
Click on the More Info button to see additional IP information.
To view additional DNS information click on the box next to the first DNS number marked '...'.
Windows NT/Me/2000/XP
- Select Start > Run. Type command into the dialog box, then click OK.
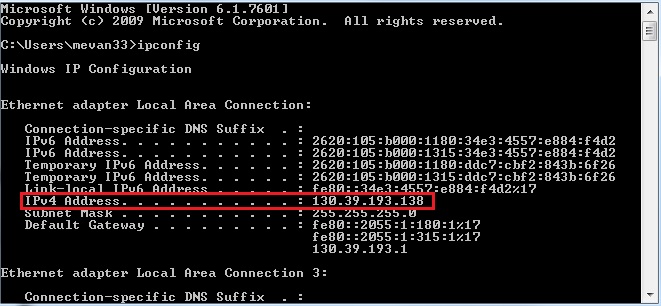
- In the resulting command line window, type ipconfig /all.
C:>ipconfig /all
Windows 2000 IP Configuration Host Name . . . . . . . . . . . . : tss-avery-babel Primary
DNS Suffix . . . . . . . : dns1.someschool.edu
Node Type . . . . . . . . . . . . : Hybrid
IP Routing Enabled. . . . . . . . : No
WINS Proxy Enabled. . . . . . . . : No
DNS Suffix Search List. . . . . . : dns1.someschool.edu
someschool.edu
Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Description . . . . . . . . . . . : 3Com EtherLink 10/100 PCI For Complete PC Management NIC (3C905C-TX)
Physical Address. . . . . . . . . : 00-01-03-AB-0E-6P
DHCP Enabled. . . . . . . . . . . : Yes
Autoconfiguration Enabled . . . . : Yes
IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.0.10
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.0.254
DHCP Server . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.0.35
DNS Servers . . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.0.12 192.168.0.13 Primary
WINS Server . . . . . . . : 192.168.0.37
Secondary WINS Server . . . . . . : 192.168.0.38
Lease Obtained. . . . . . . . . . : Wednesday, January 1, 2003 11:17:41 AM
Lease Expires . . . . . . . . . . : Friday, January 3, 2003 11:17:41 AM
The IP address will be listed in the current command line window. Other information such as the gateway address and DNS numbers will also be displayed.
Mac OS 8-9.x
Click on the Apple Menu (in the upper left corner of the display) > Control Panel > TCP/IP.
A new window will open, the TCP/IP Control Panel. This window will contain information such as IP address, subnet mask, router address (gateway), name server address (DNS) and other IP information.
Mac OS 10.x
Click on the Apple Menu > System Preferences.
Click on Network.
If the network settings are grayed out select the click the lock to make changes button. Then enter in the admin account name and password to proceed with viewing the network settings.
Choose the ethernet port by clicking the double arrows next to Show Fields and select Built in Ethernet.
Click on the TCP/IP tab.
The IP address, subnet mask, router (gateway) and domain name servers (DNS) will be displayed in the active window.
Novell 4.11-6
At the System Console screen, type config.
The last two lines of the information displayed on the screen will be the IP address and the subnet. To find the DNS numbers and gateway, follow these steps:
At the System Console screen, type loadinetcfg.nlm. The Internetworking Configuration tool will launch.
Select Protocols > TCP/IP. Press Enter and the TCP/IP Protocol Configuration window will display.
Press the down arrow to LAN Static Routing Table. Press Enter.
The default route listed will be the gateway address.
Press Esc until the TCP/IP Protocol Configuration window is again visible.
Press the down arrow to DNS Resolver Configuration. Press Enter.
The three DNS numbers, along with the name of the server, will be listed here. Press Esc four times and press Enter to exit out of inetcfg back to the main console screen.
Linux
Note: Root access may be required to run these commands. These commands will all be launched from the command line.
- Launch a command line interface. (This will vary depending on operating system distribution.)
- In the resulting command line window or screen, type ifconfig.
- Press Enter.
How To Check Modem Speed
For example:
Typing ifconfig at the command line:
How To Check Modem Ip Address Ip
[sygny@linuxbox /home]# ifconfig
Will result in something similar to the following:
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:10:5A:1A:DC:65
inet addr:198.209.253.169 Bcast:208.141.109.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:18940 errors:1 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:2
TX packets:11554 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:2 txqueuelen:100
RX bytes:4087250 (3.8 Mb) TX bytes:2499423 (2.3 Mb)
Interrupt:11 Base address:0xd000
In the example above, the IP address is labeled inet addr:198.209.253.169.
The subnet mask is listed as Mask:255.255.255.0.
Find My Router Ip Address Windows 10
The location of the gateway address can be found by typing netstat -rn at the command line. The output will look similar to:
Destination | Gateway | Genmask | Flags | MSS | Window | irrt | Iface |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
0.0.0.0 | 192.168.0.1 | 0.0.0.0 | UG | 40 | 0 | 0 | eth0 |
The gateway IP in the above instance is 192.168.0.1.
DNS information is most often found in a text file called resolv.conf. This file can be read using the cat command. A common place for this DNS file is:
/etc/resolv.conf although the name and location of this file may vary by Linux distribution.
To access this file type:
cat /etc/resolv.conf
The output will display the DNS numbers assigned to the machine, in this case:
nameserver 150.199.1.10
nameserver 150.199.8.1
Other IP Tools and Information
How To Check Modem Ip Address 192 168
http://checkip.dyndns.org — Shows the IP address of the host machine visiting the link. (May show the IP address of a firewall instead of the local machine, if the local machine is behind a firewall.)

